Spring事件发布监听机制实现业务解耦
1.引言
假设一个下单场景,订单创建成功后可能有一些后续逻辑要处理,但是和创建订单本身没有关系,此时就可以在创建订单完成后,发送一个消息,有相应部分的代码进行监听处理,避免代码耦合到一起
这样的解决思路类似于MQ,但是小项目有时候又不需要MQ这样的第三方队列来实现,那么就可以使用Spring Context包的事件发布监听的机制来进行处理
2.Spring事件发布监听机制
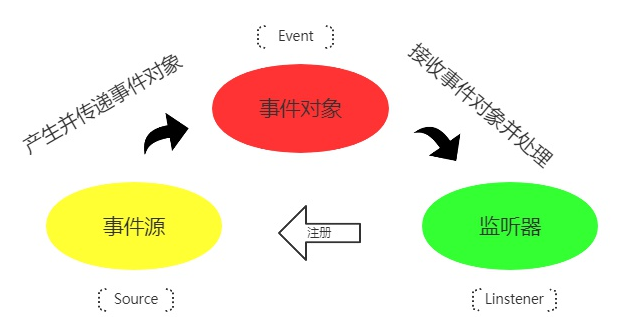
流程: 当事件源(发布者)发布事件时,相应监听此事件的监听者接收到事件对象并且进行处理
Spring的事件发布监听机制本质上就是发布-订阅,即生产者-消费者,也体现了设计模式中的观察者模式
3.三要素
- ApplicationEvent:事件
- ApplicationListener:事件监听者
- ApplicationEventPublisher:事件发布者
3.1 事件(ApplicationEvent)
消息类:
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
@Data
@Builder
public class Message {
private Long messageId;
private String content;
}事件包含的实体类
事件类:
@Getter
@Setter
public class MessageEvent extends ApplicationEvent {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 4181929072911659524L;
private Message message;
public MessageEvent(Message message) {
super(message);
this.message = message;
}
}事件类,继承了ApplicationEvent,并且包含了传递实体类Message
MessageEvent的关系类图(Diagram):
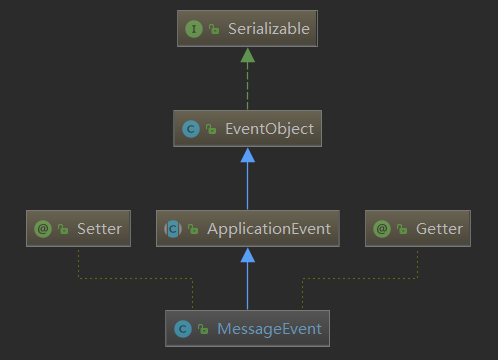
其中ApplicationEvent的源码:
\**
* Class to be extended by all application events. Abstract as it
* doesn't make sense for generic events to be published directly.
*
* @author Rod Johnson
* @author Juergen Hoeller
* @see org.springframework.context.ApplicationListener
* @see org.springframework.context.event.EventListener
*\
public abstract class ApplicationEvent extends EventObject {
\** use serialVersionUID from Spring 1.2 for interoperability. *\
private static final long serialVersionUID = 7099057708183571937L;
\** System time when the event happened. *\
private final long timestamp;
\**
* Create a new {@code ApplicationEvent}.
* @param source the object on which the event initially occurred or with
* which the event is associated (never {@code null})
*\
public ApplicationEvent(Object source) {
super(source);
this.timestamp = System.currentTimeMillis();
}
\**
* Return the system time in milliseconds when the event occurred.
*\
public final long getTimestamp() {
return this.timestamp;
}
}可以看出ApplicationEvent有记录发生event的时间,并且source的意义就是当做发布事件的实体类
3.2 事件监听者(ApplicationListener)
事件监听类:方式一(EventListener注解实现)
@Component
@Slf4j
public class MessageListener {
@EventListener(value = MessageEvent.class)
public void listen(MessageEvent event){
log.info("\n██listener1线程:{}",Thread.currentThread().getThreadGroup()+ "\" +Thread.currentThread().getName());
log.info("event:{}",event);
\\ 处理逻辑
}
}注解实现监听的原理:
1:查看@EventListener注解的调用链,其中EventListenerMethodProcessor类的processBean方法(1)
\\ 截取的代码
Map<Method, EventListener> annotatedMethods = null;
try {
annotatedMethods = MethodIntrospector.selectMethods(targetType,
(MethodIntrospector.MetadataLookup<EventListener>) method ->
AnnotatedElementUtils.findMergedAnnotation(method, EventListener.class));
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
\\ An unresolvable type in a method signature, probably from a lazy bean - let's ignore it.
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Could not resolve methods for bean with name '" + beanName + "'", ex);
}
}获取所有被
@EventListener注解修饰的Listener
2:EventListenerMethodProcessor类的processBean方法(2)
\\ 截取的代码
\\ Non-empty set of methods
ConfigurableApplicationContext context = this.applicationContext;
Assert.state(context != null, "No ApplicationContext set");
List<EventListenerFactory> factories = this.eventListenerFactories;
Assert.state(factories != null, "EventListenerFactory List not initialized");
for (Method method : annotatedMethods.keySet()) {
for (EventListenerFactory factory : factories) {
if (factory.supportsMethod(method)) {
Method methodToUse = AopUtils.selectInvocableMethod(method, context.getType(beanName));
ApplicationListener<?> applicationListener =
factory.createApplicationListener(beanName, targetType, methodToUse);
if (applicationListener instanceof ApplicationListenerMethodAdapter) {
((ApplicationListenerMethodAdapter) applicationListener).init(context, this.evaluator);
}
context.addApplicationListener(applicationListener);
break;
}
}
}使用Listener Factory类生产出所有被
@EventListener的类注入进Spring Context
事件监听类:方式二(实现ApplicationListener接口)
@Component
@Slf4j
public class MessageListener2 implements ApplicationListener<MessageEvent> {
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(MessageEvent event) {
log.info("\n██listener2线程:{}",Thread.currentThread().getThreadGroup()+ "\" +Thread.currentThread().getName());
log.info("event:{}",event);
\\ 处理逻辑
}
}实现接口来实现监听的原理:
1:ApplicationListenerDetector的postProcessAfterInitialization方法
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) {
if (bean instanceof ApplicationListener) {
\\ potentially not detected as a listener by getBeanNamesForType retrieval
Boolean flag = this.singletonNames.get(beanName);
if (Boolean.TRUE.equals(flag)) {
\\ singleton bean (top-level or inner): register on the fly
this.applicationContext.addApplicationListener((ApplicationListener<?>) bean);
}
else if (Boolean.FALSE.equals(flag)) {
if (logger.isWarnEnabled() && !this.applicationContext.containsBean(beanName)) {
\\ inner bean with other scope - can't reliably process events
logger.warn("Inner bean '" + beanName + "' implements ApplicationListener interface " +
"but is not reachable for event multicasting by its containing ApplicationContext " +
"because it does not have singleton scope. Only top-level listener beans are allowed " +
"to be of non-singleton scope.");
}
this.singletonNames.remove(beanName);
}
}
return bean;
}判断一个Bean如果是ApplicationListener,则也是使用context.addApplicationListener添加
总结: 相对于实现ApplicationListener接口来监听事件的方式,使用注解的方式更加简便,并且方式二一个监听类只能监听一个事件,方式一则可新增方法来监听多个其他的事件
3.3 事件发布者(ApplicationEventPublisher)
@Autowired
private ApplicationContext applicationContext;
@PostMapping("\sendMessage")
public String sendMessage(){
log.info("\n██Test线程:{}",Thread.currentThread().getThreadGroup()+ "\" +Thread.currentThread().getName());
Message newMessage = Message.builder()
.messageId(20200610111500000L)
.content("消息内容").build();
MessageEvent event = new MessageEvent(newMessage);
\\ 事件发布
applicationContext.publishEvent(event);
return "消息发送成功";
}事件发布原理分析:
1:查看ApplicationContext类
public interface ApplicationContext extends EnvironmentCapable, ListableBeanFactory, HierarchicalBeanFactory,
MessageSource, ApplicationEventPublisher, ResourcePatternResolver {ApplicationContext实现了ApplicationEventPublisher类的pulish方法,ApplicationContext的抽象类AbstractApplicationContext里阐述了具体的publishEvent方法
2:AbstractApplicationContext类的publishEvent方法
protected void publishEvent(Object event, @Nullable ResolvableType eventType) {
Assert.notNull(event, "Event must not be null");
\\ Decorate event as an ApplicationEvent if necessary
ApplicationEvent applicationEvent;
if (event instanceof ApplicationEvent) {
applicationEvent = (ApplicationEvent) event;
}
else {
applicationEvent = new PayloadApplicationEvent<>(this, event);
if (eventType == null) {
eventType = ((PayloadApplicationEvent<?>) applicationEvent).getResolvableType();
}
}
\\ Multicast right now if possible - or lazily once the multicaster is initialized
if (this.earlyApplicationEvents != null) {
this.earlyApplicationEvents.add(applicationEvent);
}
else {
getApplicationEventMulticaster().multicastEvent(applicationEvent, eventType);
}
\\ Publish event via parent context as well...
if (this.parent != null) {
if (this.parent instanceof AbstractApplicationContext) {
((AbstractApplicationContext) this.parent).publishEvent(event, eventType);
}
else {
this.parent.publishEvent(event);
}
}
}getApplicationEventMulticaster().multicastEvent方法可以看出事件是通过SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster的multicastEvent方法发布的
3:SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster的multicastEvent方法
@Override
public void multicastEvent(final ApplicationEvent event, @Nullable ResolvableType eventType) {
ResolvableType type = (eventType != null ? eventType : resolveDefaultEventType(event));
Executor executor = getTaskExecutor();
for (ApplicationListener<?> listener : getApplicationListeners(event, type)) {
if (executor != null) {
executor.execute(() -> invokeListener(listener, event));
}
else {
invokeListener(listener, event);
}
}
}可以看出如果设置了Executor(线程池)的话,则异步执行监听方法,否则执行同步方法
所以后续可以用设置Executor的方法实现异步
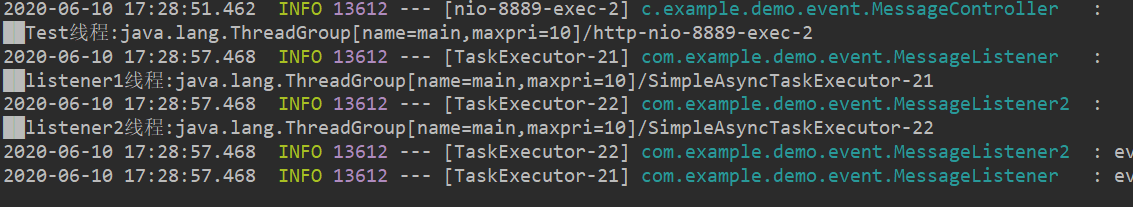
4.测试
Postman调用sendMessage接口,成功实现功能
5.支持异步
5.1 设置Executor的方法实现异步(推荐)
@Slf4j
@Configuration
public class EventConfig {
@Bean(name = "applicationEventMulticaster")
public ApplicationEventMulticaster simpleApplicationEventMulticaster() {
SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster eventMulticaster
= new SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster();
eventMulticaster.setTaskExecutor(new SimpleAsyncTaskExecutor());
return eventMulticaster;
}
}5.2 异步注解
1:主类新增@EnableAsync注解开启异步
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableAsync
public class SpringEventDemoApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SpringEventDemoApplication.class, args);
}
}2:监听类监听方法新增注解@Async
@Component
@Slf4j
public class MessageListener {
@Async
@EventListener(value = MessageEvent.class)
public void listen(MessageEvent event){
ThreadUtil.sleep(6000);
log.info("\n██listener1线程:{}",Thread.currentThread().getThreadGroup()+ "\" +Thread.currentThread().getName());
log.info("event:{}",event);
}
}这种做法可以实现异步,但是其实有点违背了Spring事件机制的设计初衷,所以推荐第一种做法实现异步
6.Demo代码
参考链接:
Spring事件监听机制 - 知乎
深入浅出Spring\SpringBoot 事件监听机制 - 知乎
Spring事件发布监听
spring 事件及异步方法使用

